TAT probes are heated on the ground.
On the ground, the TAT probes are not heated and pitot heating operates at a low level (the changeover to normal power in flight is automatic).
The drain masts are heated after first engine start.
Drain masts are heated when electrical system is powered. Low level on ground and high level in flight.
In the event of loss of electrical supply the engine anti-ice valve:
At what power level does window heat operate while airborne?

The electric windshield wipers are controlled:
When a pneumatic leak is detected, the wing anti-ice valves:
What happens when either engine anti-ice is open?

When wing anti-ice is selected, the N1 or EPR limit is automatically reduced, and the idle N1 or EPR is automatically increased.
When either engine anti-ice valve is open:
 A.Lesik
A.Lesik
When wing anti-ice is selected, the N1 or EPR limit is automatically reduced, and the idle N1 or EPR is automatically increased.
Electrical heating is provided for the protection of:

The probe heaters can be activated manually prior to engine start by placing the PROBE/WINDOW HEAT pushbutton.
Advertisement
What is the speed limit to operate the windscreen wipers?
How is cockpit window heating regulated?
Where do the wing anti-ice indications appear on ECAM?
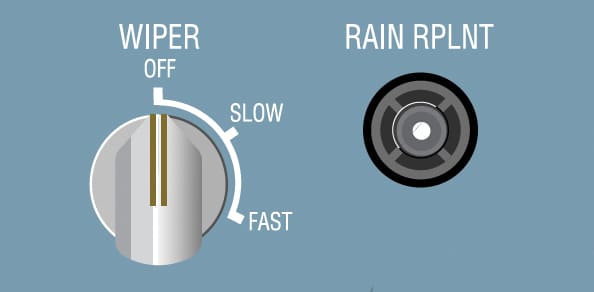
When the wiper is turned off:
The engine nacelle is anti-iced by:

When the flight crew pushes the rain repellent button, the timer applies a measured quantity of rain repellent to the windshield. To repeat the cycle, the flight crew must push the button again.
On the ground the wing anti-ice valves will:
The _____ on each wing are anti-iced with pneumatic bleed air.
In flight, hot air from the pneumatic system heats the three outboard slats (3-4-5) of each wing. Air is supplied through one valve in each wing.
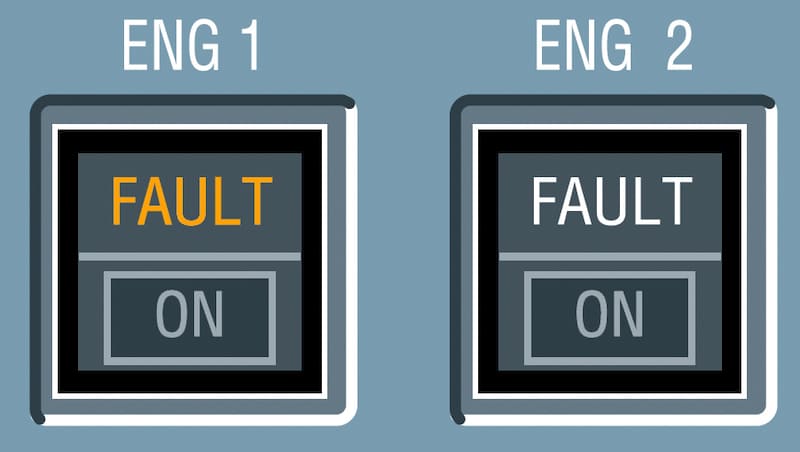
The FAULT light on one engine anti-ice switch indicates the valve:
With reference to the PROBE/WINDOW HEAT pb, which of the following is true?

Window heating comes on automatically when at least one engine is running, or when the aircraft is in flight. Manually, when PROBE/WINDOW HEAT pb is ON. Windshield heating operates at low power on the ground and at normal power in flight. Only one heating level exists for the windows.
Advertisement
The aircraft uses electrical heating for anti-icing each windshield and cockpit side windows.

The aircraft uses electrical heating for anti-icing each windshield and defogging the cockpit side windows.
In the event of an electrical power loss:
The wipers can operate at different speeds:
The RAIN RPLNT (rain repellent) pb is inhibited on the ground when the engines are stopped.

The ON light illuminates on the wing anti-ice pb:
Window heat operates at what power level in flight?
In moderate to heavy rain, the flight crew can spray a rain repellent liquid on the windshield to improve visibility. After about _____, the windows are covered with spray.

Separate pushbuttons control rain repellent application on each side of the windshield.
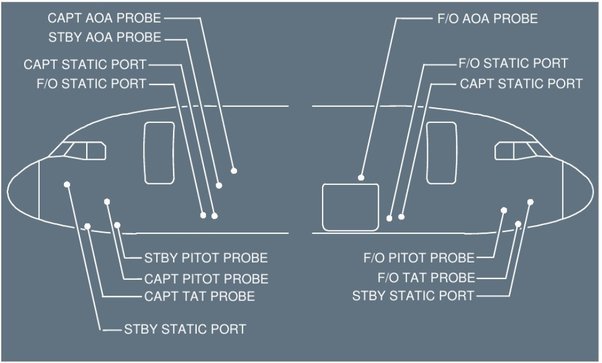
There are _____ independent Probe Heat Computers (PHCs) automatically control and monitor Captain probes, F/O probes and STBY probes.

They protect against overheating and indicate faults.
Only one heating level exists for the cockpit windows.
 A.Pecci
A.Pecci
With the loss of electrical power the wing anti-ice valves:
Advertisement
The Window Heat Computer provides two power levels for the windshield:

What is the difference between the engine and wing anti-ice fault lights?

What happens to the heat at the drain masts when the aircraft is on the ground?
If one engine anti-ice system fails, the second one takes over and provides anti-icing for both engines.
When the aircraft is on ground, the flight crew can initiate a 30 s wing anti-ice test sequence by turning the system ON.

Probe heat comes on automatically when:
Probe heat comes on automatically when at least one engine is running, or when the aircraft is in flight. Manually, when PROBE/WINDOW HEAT pb is ON. On ground, TAT probes are not heated and pitot heating operates at a low level.
