The BATT DIR busses are displayed on the ELEC synoptic page but not on the EICAS.
Correct!
Wrong!
The BATT DIR busses are not displayed on the ELEC synoptic page.
Power isolation and distribution for the electrical system is managed by Four Electrical Power Centers (EPCs). The EPCs contain the AC and DC busses, the TRUs, the line and bus tie contactors, and most of thermal circuit breakers on the aircraft.
Correct!
Wrong!
When the L DISC or R DISC guarded switch is pushed, the corresponding VFG disconnects from the gearbox.
Correct!
Wrong!
Each battery charger monitors battery temperature to determine the appropriate charging threshold and inhibits charging if the battery temperature exceeds this threshold.
Correct!
Wrong!
The DC EMER bus and the BATT DIR busses are:
Correct!
Wrong!
Engine VFG high oil temperature has two thresholds. When the temperature reaches the first threshold, the amber OIL light comes on in the corresponding switch. When the temperature is at the higher limit threshold, the engine VFG automatically disconnects from the engine accessory gearbox.
Correct!
Wrong!
If there is a full loss of AC power in-flight, the RAT deploys automatically _____. The flight crew can also manually deploy the RAT with the guarded RAT GEN switch on the overhead ELECTRICAL panel.
Correct!
Wrong!
When the RAT is deployed, the advisory message RAT DPLY is displayed on the EICAS page.
When the EXT PWR switch on the ELECTRICAL panel is pushed, the external power mode is in operation. In external mode, all of the electrical system is powered.
Correct!
Wrong!
If the aircraft is not powered by an external AC source, both batteries are needed to start the APU.
Correct!
Wrong!
Three Transformer Rectifier Units (TRUs) and _____ supply the required DC power.
Correct!
Wrong!
Advertisement
There are two identical AC battery chargers in the mid equipment bay.
Correct!
Wrong!
The RAT supplies hydraulic power at speeds as low as _____.
Correct!
Wrong!
The RAT is a two-bladed, wind-driven turbine that powers a 115 VAC, air-cooled generator, rated at 10 kVA. It also drives:
Correct!
Wrong!
If only batteries supply the power for more than _____, the 'BATT DISCHARGING' caution message is displayed on the EICAS page. A horn also sounds until AC power is available or batteries are switched off.
Correct!
Wrong!
Three dedicated Permanent Magnet Alternator/Generators (PMAGs) supply power to two Fly-By-Wire Power Converters (FBWPCs) for the fly-by-wire components.
Correct!
Wrong!
There are two dedicated Permanent Magnet Alternator/Generators (PMAGs)that supply power to two Fly-By-Wire Power Converters (FBWPCs) for the fly-by-wire components.
The RAT supplies electrical power at aircraft speeds of _____ or more.
Correct!
Wrong!
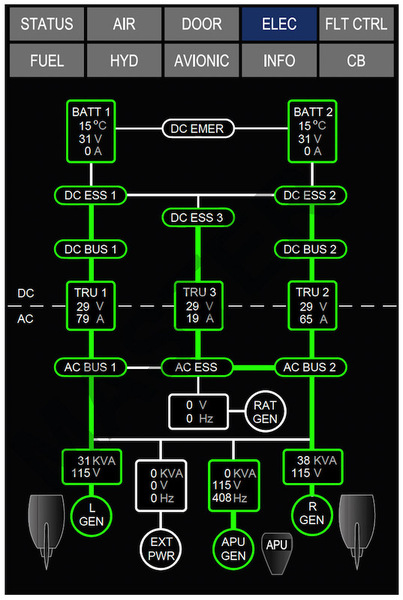
The batteries connect to the DC ESS 1 and DC ESS 2 busses, and all three DC ESS busses are connected in parallel.
Correct!
Wrong!
If there is full loss of AC power, the Ram Air Turbine (RAT) supplies _____. The RAT is stowed in the right side of the wing-to-body fairing near the right main landing gear.
Correct!
Wrong!
Three Transformer Rectifier Units (TRUs) are the primary source of DC power, and are each rated at 350 amperes. The TRUs receive 115 VAC power from the AC busses, convert it to 28 VDC, and distribute it to the DC busses.
Correct!
Wrong!
DC power for the aircraft is supplied by:
Correct!
Wrong!
Advertisement
If a single VFG is recovered while the RAT is deployed, the VFG supplies the entire electrical system except for the _____. The RAT continues to supply these two busses.
Correct!
Wrong!
If a second VFG is recovered, the electrical system is powered normally, with the exception that the RAT continues to supply the AC ESS bus and DC ESS 3 bus.
The electrical control and distribution system is divided into three Electrical Power Centers (EPCs) that are managed by the Bus Power Control Units (BPCUs) and an Emergency Power Control (EMPC).
Correct!
Wrong!
Airbus A220 – Electrical
